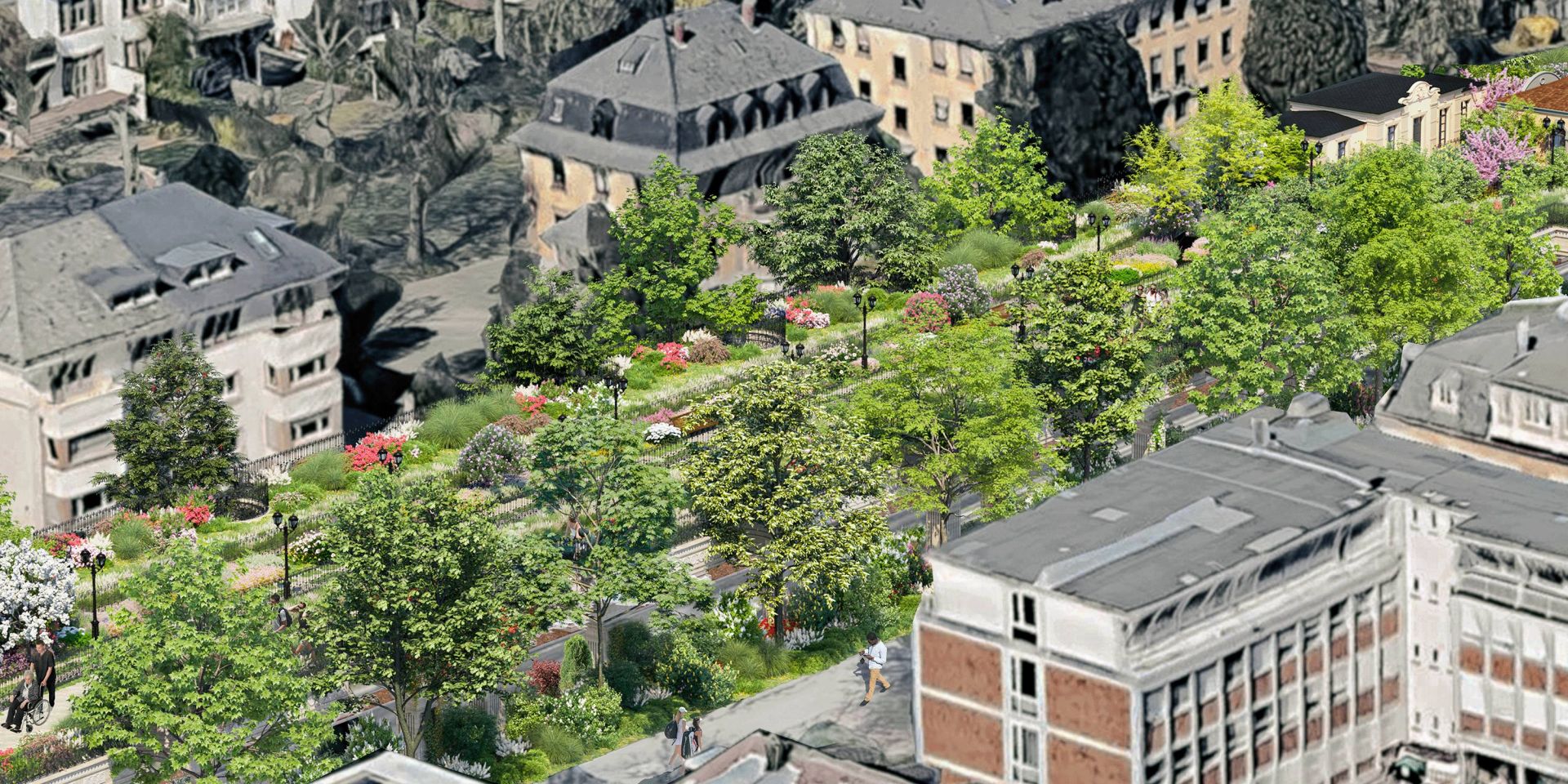
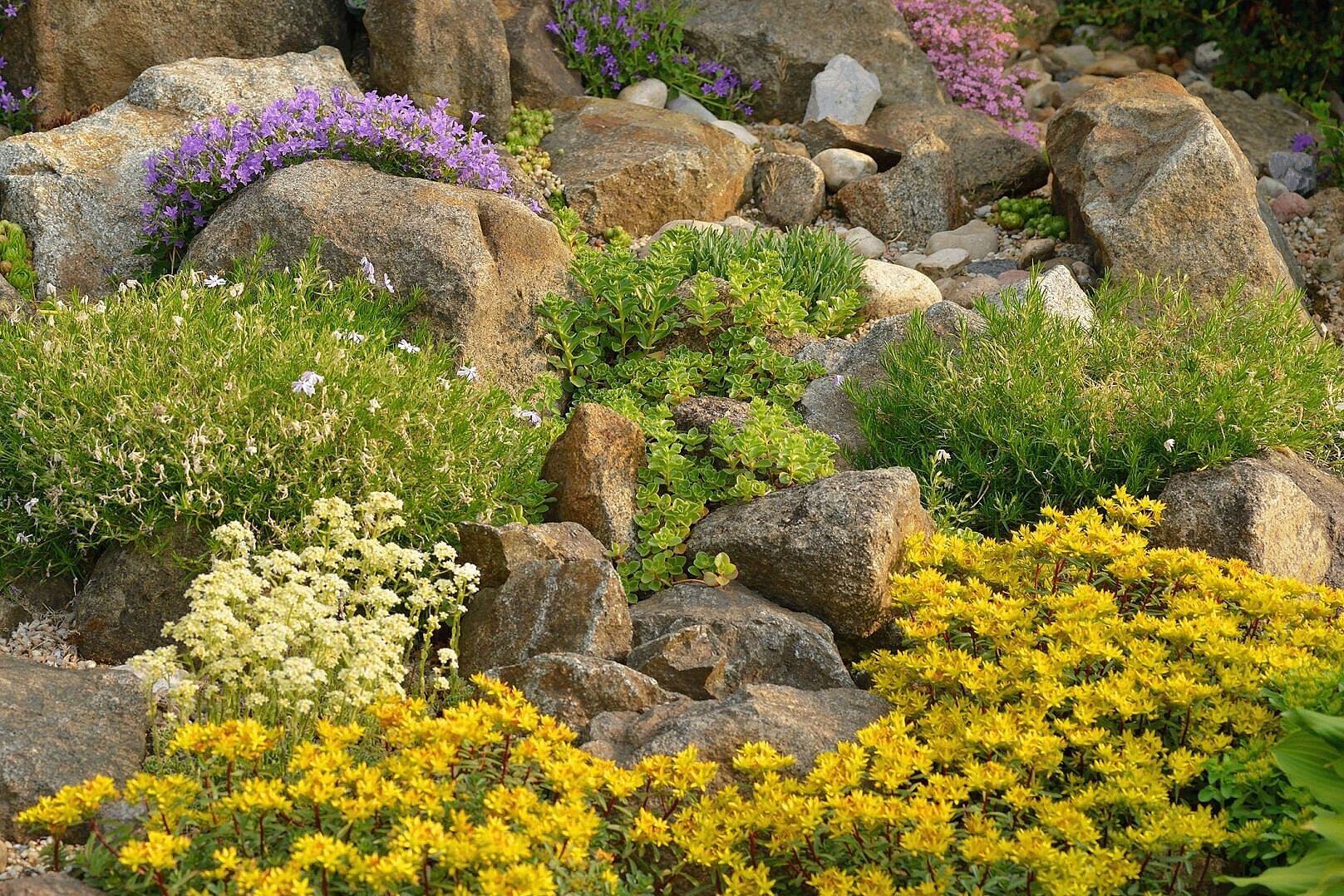
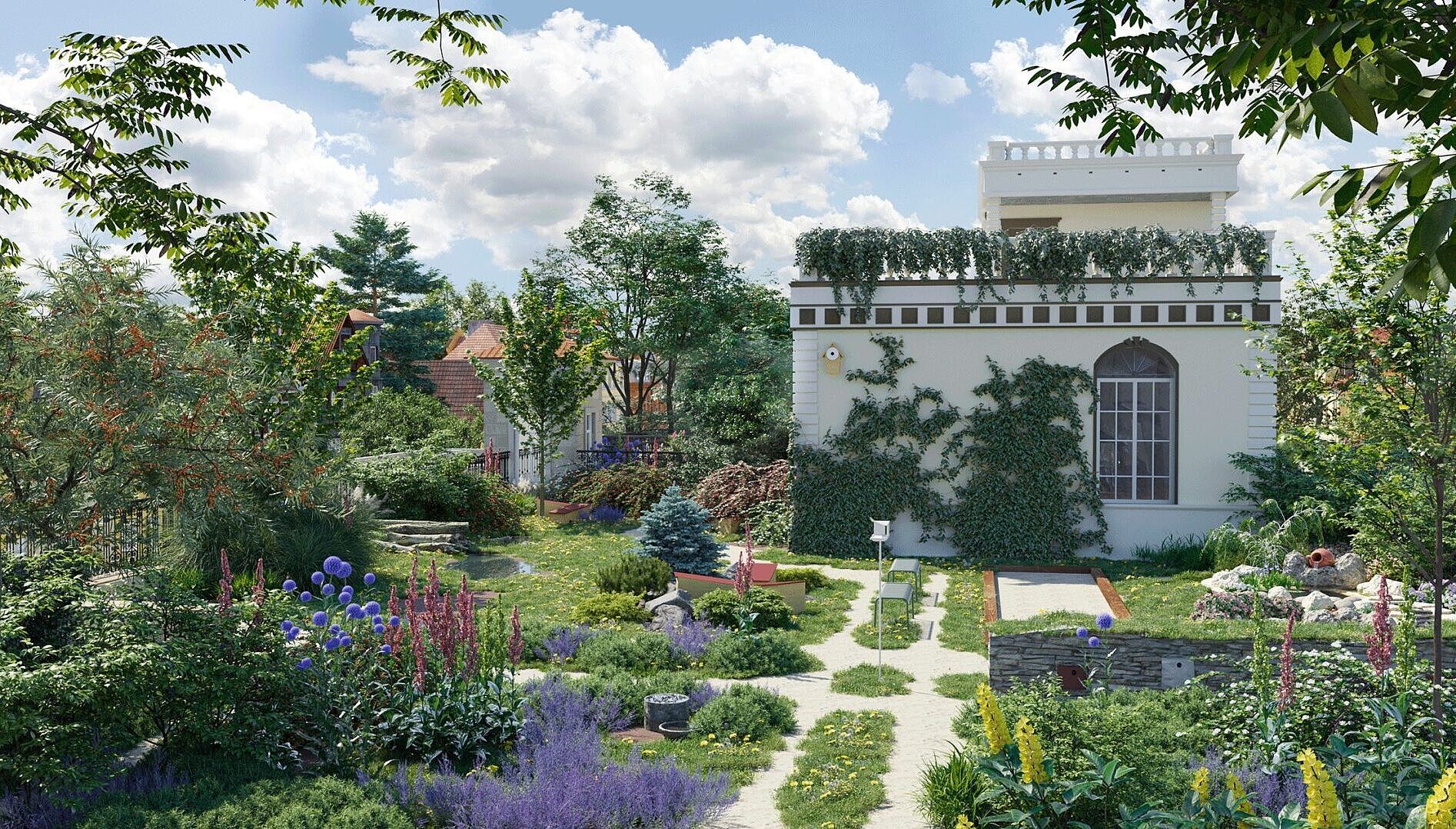
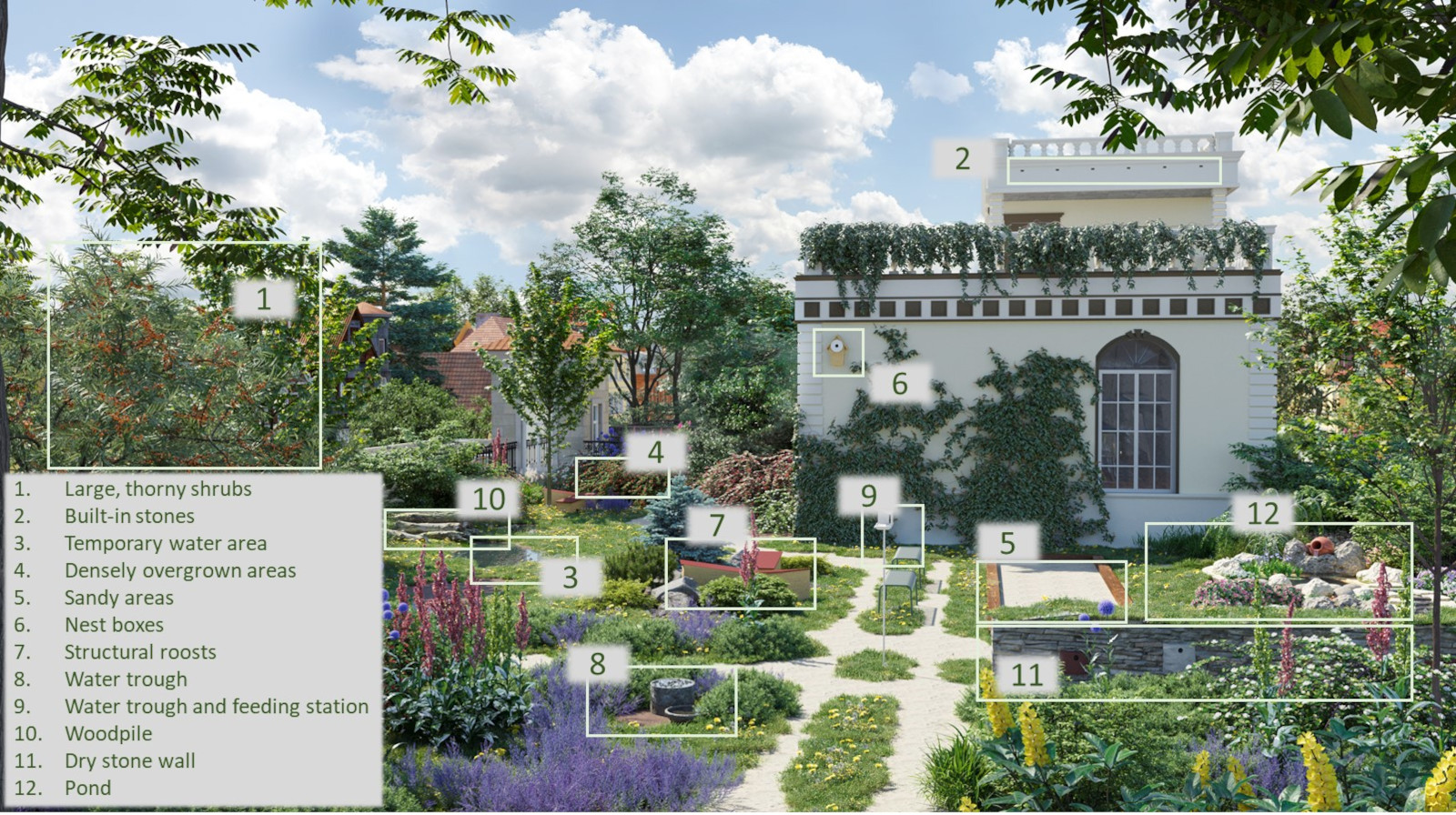
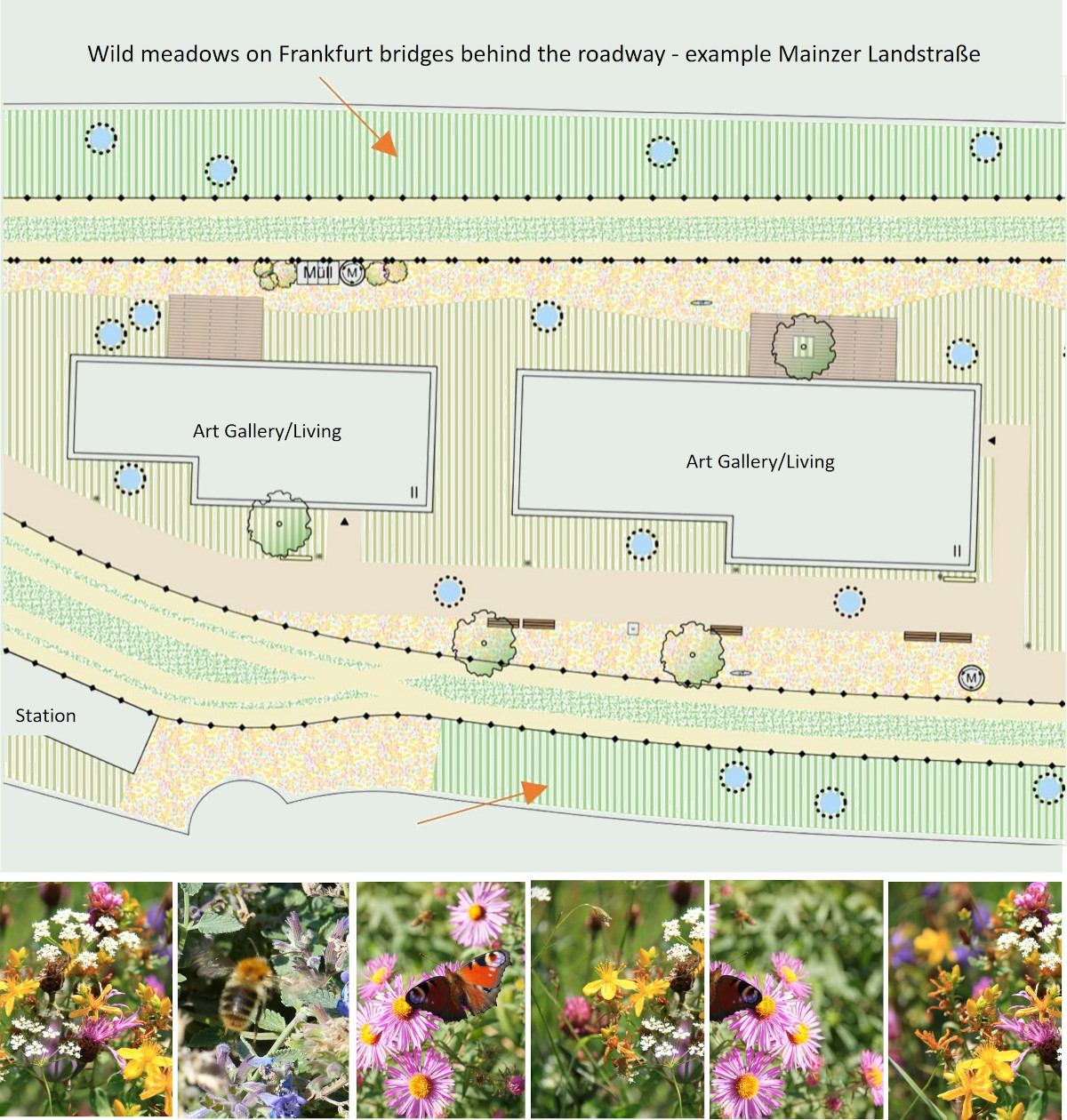
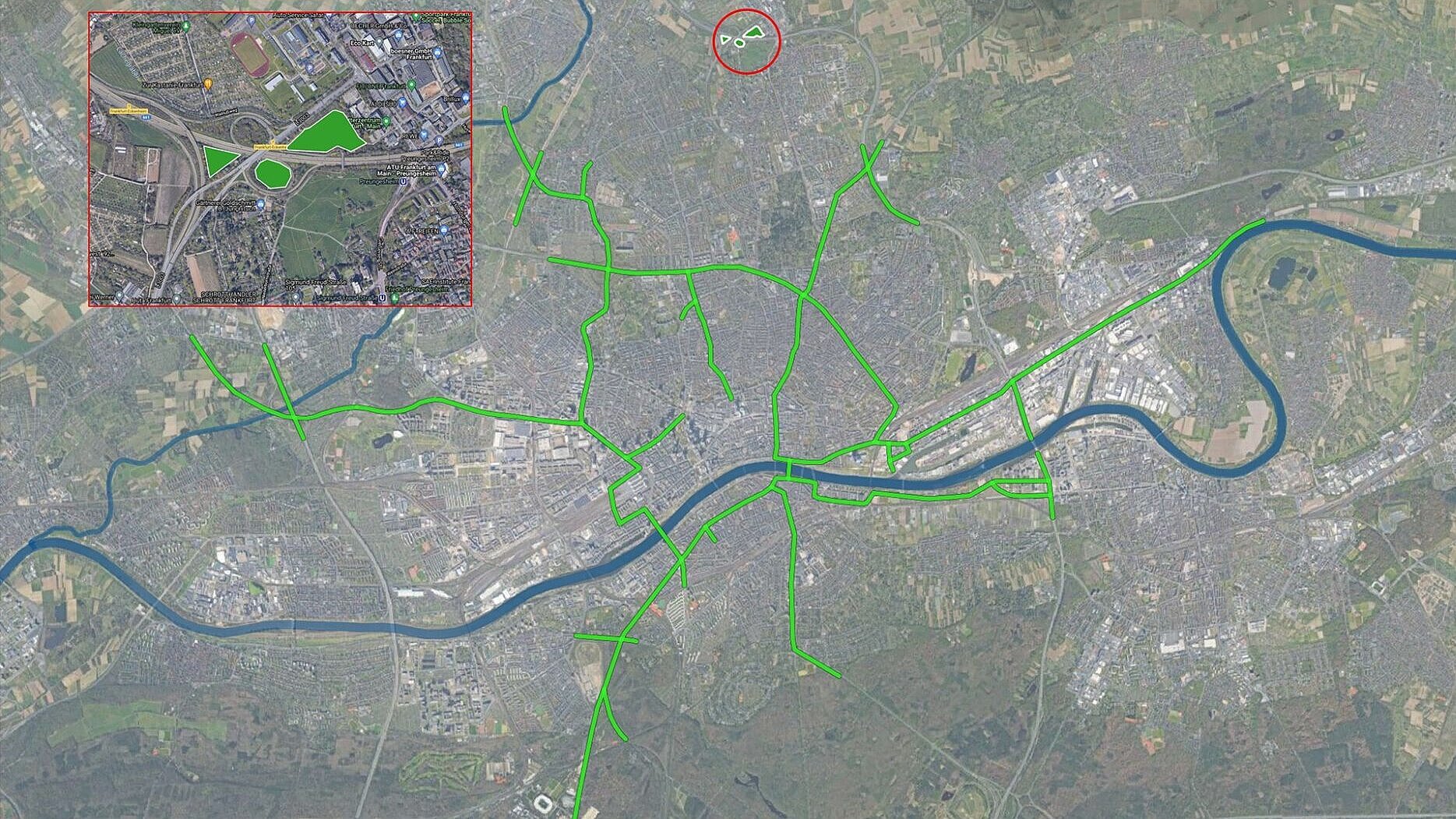
Content: The network of bridges offers new habitats and a stepping stone biotope structure with its diverse green spaces
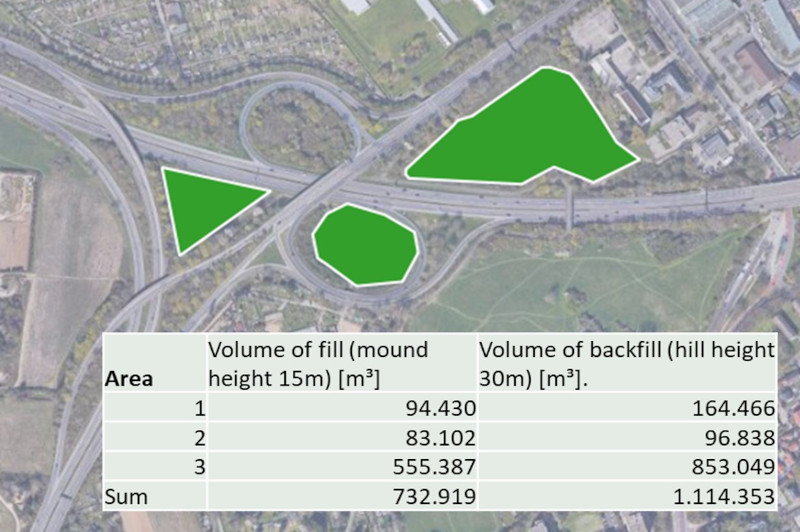
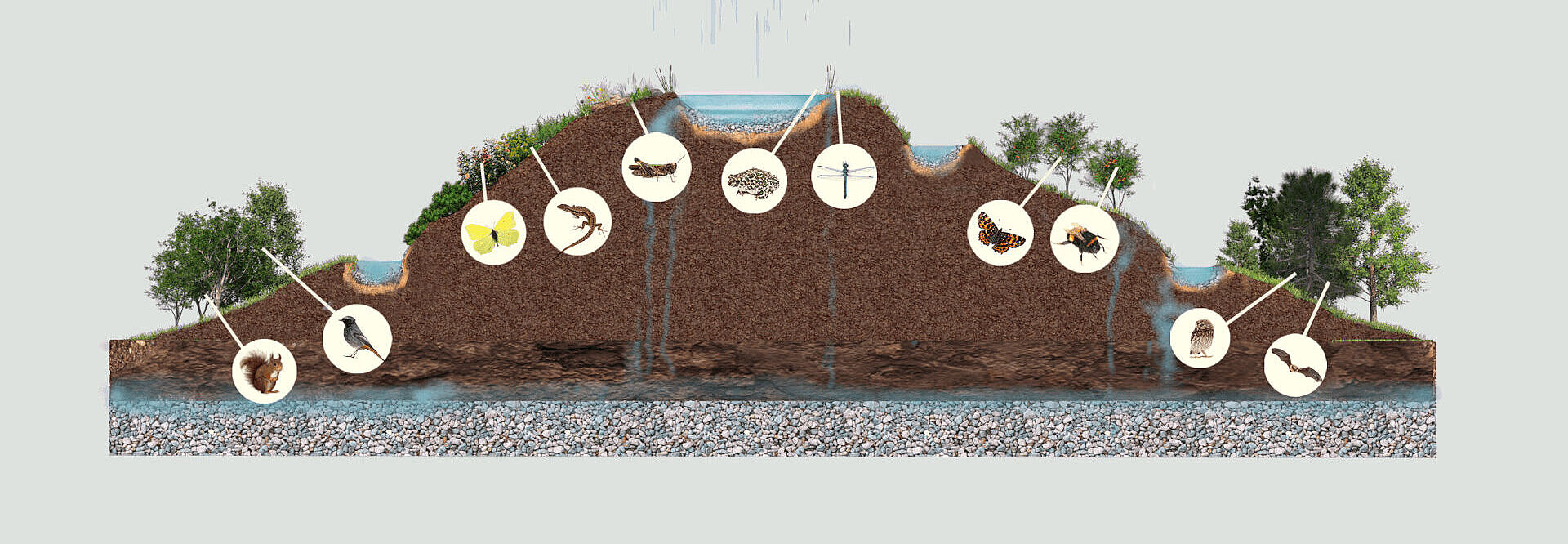
Already during the construction of the bridges, nesting, breeding and staging areas for animals and insects are created on the bridges; and the excavated material produced during the construction project is used directly to create nature conservation mounds.
Thus, in the course of a major construction project, new habitats are simultaneously created for Frankfurt's flora and fauna.
Moreover, stepping stone biotopes are created: birds, butterflies, smaller mammals, but also bats can cross gray roads with the help of the green bridges.